Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a critical life-saving skill that anyone can learn. When an adult suffers cardiac arrest, immediate action can dramatically increase the chances of survival. First Aid, CPR, and BLS training teaches individuals how to respond effectively, giving bystanders the confidence to step in during emergencies.
Performing CPR promptly helps maintain blood flow to vital organs, particularly the brain and heart, until professional medical care arrives. Understanding how to help someone in this critical moment can make the difference between life and death.
Recognizing When CPR Is Needed
The first step in adult CPR is knowing when to act. Quick recognition of cardiac arrest ensures that life-saving measures begin without delay.
Signs to watch for include:
- Sudden unresponsiveness or loss of consciousness
- Absence of normal breathing or irregular gasping
- No detectable pulse or signs of circulation
- Collapse following chest pain, shortness of breath, or dizziness
Being alert to these symptoms enables you to act decisively and shows practical knowledge of how to save lives in high-pressure situations.
Preparing to Perform CPR
Before performing CPR, ensuring safety and readiness is essential. Proper preparation improves effectiveness and reduces risk to both rescuer and victim.
Steps include:
- Checking the environment for hazards to ensure both you and the victim are safe
- Wearing gloves if available to reduce contamination
- Positioning the victim on their back on a firm, flat surface
- Removing restrictive clothing from the chest area to allow for effective compressions
Preparation sets the foundation for effective CPR and demonstrates a structured approach to First Aid and BLS.
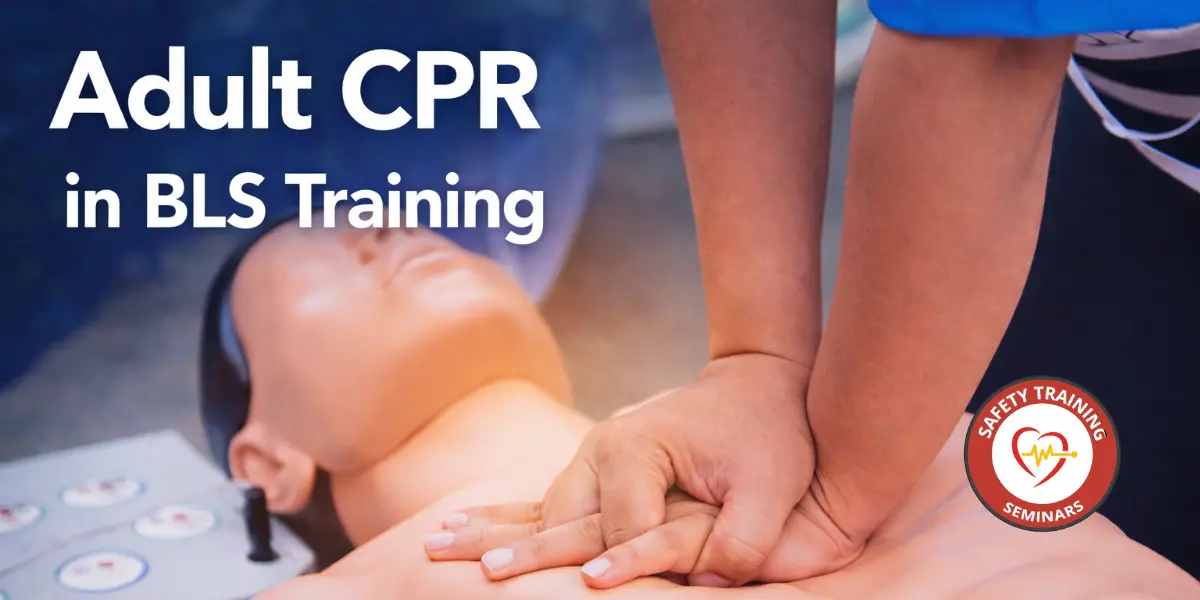
Performing Chest Compressions
Chest compressions are the cornerstone of adult CPR. They maintain circulation to vital organs, buying time until professional help arrives.
Key steps for effective compressions:
- Place the heel of one hand in the center of the victim’s chest, with the other hand on top, interlocking fingers
- Keep arms straight and shoulders directly above your hands
- Push hard and fast, compressing the chest at least 2 inches deep at a rate of 100–120 compressions per minute
- Allow the chest to fully recoil between compressions
- Continue uninterrupted unless giving rescue breaths or using an emergency device
Proper compressions demonstrate how to help someone by maintaining life-sustaining circulation.
Integrating Rescue Breaths
Rescue breaths complement chest compressions by supplying oxygen to the lungs and bloodstream. They are a key component of BLS training for adults.
Steps to deliver rescue breaths:
- After 30 compressions, open the airway using the head-tilt, chin-lift method
- Pinch the victim’s nose shut and seal your mouth over theirs
- Deliver 2 slow, full breaths, watching for chest rise
- Resume compressions immediately after breaths
- Repeat the cycle of 30 compressions and 2 breaths until the victim regains consciousness or emergency help arrives
Effective integration of compressions and breaths maximizes the chances of survival, showing exactly how to save someone in cardiac arrest.
Using Emergency Tools During CPR
In a BLS scenario, tools such as barrier devices and automated external defibrillators (AEDs) may be available. Proper use enhances CPR effectiveness.
Key points include:
- Barrier devices provide protection while delivering rescue breaths
- AEDs analyze heart rhythm and deliver shocks if necessary
- Place the AED pads according to instructions while continuing CPR until prompted
- Follow device prompts carefully for timing and safety
- Maintain CPR efforts between AED analyses
Using these tools demonstrates advanced knowledge of First Aid and BLS and shows practical ways how to help in emergencies.
Monitoring and Responding to Changes
CPR is not a one-time action; ongoing monitoring ensures continued effectiveness. Victims may regain signs of life or deteriorate unexpectedly, requiring adaptation.
Monitoring includes:
- Checking for normal breathing and responsiveness after each CPR cycle
- Observing for signs of circulation such as coughing, movement, or eye-opening
- Being ready to resume compressions immediately if necessary
- Providing reassurance and support to the victim once they regain consciousness
Continuous observation is crucial for how to save lives and reflects proper BLS protocols in real-world emergencies.
Practicing CPR for Confidence and Preparedness
The most effective CPR occurs when responders are trained and confident. Regular practice through BLS courses ensures that techniques are second nature during emergencies.
Benefits of practice include:
- Faster response time in cardiac arrest situations
- Correct technique with proper compression depth and rhythm
- Confidence in combining compressions and rescue breaths
- Awareness of how to use emergency tools like AEDs effectively
Training transforms bystanders into capable responders, reinforcing how to help in critical moments.
Educating Others on Life-Saving CPR Skills
Community awareness and education empower more people to act during emergencies. Teaching CPR, First Aid, and BLS ensures that bystanders can provide immediate assistance, improving overall survival rates.
Community benefits include:
- Reducing fatalities from sudden cardiac arrest
- Creating safer workplaces, schools, and public spaces
- Encouraging proactive action instead of hesitation
- Promoting a culture of preparedness and confidence
Sharing knowledge about CPR helps others understand how to save lives effectively and responsibly.

Final Thoughts: Quick Action Can Save a Life
Adult CPR is a critical skill that can prevent death and severe injury during cardiac emergencies. By recognizing cardiac arrest, preparing the victim, performing compressions and breaths, using emergency tools, and monitoring the patient, you can make a tangible difference.
Safety Training Seminars provides comprehensive BLS training that equips participants with the knowledge and confidence to respond effectively. Knowing how to help someone in cardiac arrest transforms bystanders into life-saving responders. Every second matters, and proper action can truly save a life.